No matter what kind of neurovascular challenge you face, we are prepared to support you with state-of-the art screening technologies, advanced therapies and the latest endovascular options. These conditions can develop over time or come without warning, and sometimes can be life-threatening emergencies. Whether you have an aneurysm or a rare blood-vessel disorder, we as endovascular Interventional specialists can provide the care you need.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes.
A stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and other complications.
The good news is that many fewer Indians die of stroke now than in the past. Effective treatments can also help prevent disability from stroke.
Many factors can increase your stroke risk. Potentially treatable stroke risk factors include:
- Lifestyle risk factors
- Being overweight or obese
- Physical inactivity
- Heavy or binge drinking
- Use of illegal drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamine
- Medical risk factors
- High blood pressure
- Cigarette smoking or secondhand smoke exposure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart failure, heart defects, heart infection or abnormal heart rhythm, such as atrial fibrillation
- Personal or family history of stroke, heart attack or transient ischemic attack
- Other factors associated with a higher risk of stroke include:
- Age — People age 55 or older have a higher risk of stroke than do younger people.
- Race — African Americans have a higher risk of stroke than do people of other races.
- Sex — Men have a higher risk of stroke than women. Women are usually older when they have strokes, and they're more likely to die of strokes than are men.
- Hormones — Use of birth control pills or hormone therapies that include estrogen increases risk.
If you or someone you're with may be having a stroke, pay particular attention to the time the symptoms began. Some treatment options are most effective when given soon after a stroke begins.
Signs and symptoms of stroke include:
- Trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying. You may experience confusion, slur your words or have difficulty understanding speech.
- Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm or leg. You may develop sudden numbness, weakness or paralysis in your face, arm or leg. This often affects just one side of your body. Try to raise both your arms over your head at the same time. If one arm begins to fall, you may be having a stroke. Also, one side of your mouth may droop when you try to smile.
- Problems seeing in one or both eyes. You may suddenly have blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes, or you may see double.
- Headache. A sudden, severe headache, which may be accompanied by vomiting, dizziness or altered consciousness, may indicate that you're having a stroke.
- Trouble walking. You may stumble or lose your balance. You may also have sudden dizziness or a loss of coordination.
A stroke can sometimes cause temporary or permanent disabilities, depending on how long the brain lacks blood flow and which part was affected. Complications may include:
- Paralysis or loss of muscle movement. You may become paralyzed on one side of your body, or lose control of certain muscles, such as those on one side of your face or one arm.
- Difficulty talking or swallowing. A stroke might affect control of the muscles in your mouth and throat, making it difficult for you to talk clearly, swallow or eat. You also may have difficulty with language, including speaking or understanding speech, reading, or writing.
- Memory loss or thinking difficulties. Many people who have had strokes experience some memory loss. Others may have difficulty thinking, reasoning, making judgments and understanding concepts.
- Emotional problems. People who have had strokes may have more difficulty controlling their emotions, or they may develop depression.
- Pain. Pain, numbness or other unusual sensations may occur in the parts of the body affected by stroke. For example, if a stroke causes you to lose feeling in your left arm, you may develop an uncomfortable tingling sensation in that arm.
- Changes in behavior and self-care ability. People who have had strokes may become more withdrawn. They may need help with grooming and daily chores.
Seek immediate medical attention if you notice any signs or symptoms of a stroke, even if they seem to come and go or they disappear completely. Think 'FAST' and do the following:
- Face. Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face droop?
- Arms. Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward? Or is one arm unable to rise?
- Speech. Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is his or her speech slurred or strange?
- Time. If you observe any of these signs, call for emergency medical help immediately.
The treatment for ischemic stroke is clot removal. Vascular and Interventional Radiologist can accomplish this with medication and mechanical treatments:
- Medical Treatment with Alteplase IV r-tPA
Considered the gold standard, tissue plasminogen activator – r-tPA (otherwise known as alteplase) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat ischemic stroke, which is caused when a vessel supplying blood to the brain is blocked. - Doctors administer Alteplase IV r-tPA through an IV in the arm, dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived. Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke. So it’s important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately.
An endovascular procedure or a mechanical thrombectomy is a strongly recommended option to remove a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion or LVO.
The procedure:
- Should be done within six hours of onset of acute stroke symptoms.
- Can benefit patients under certain conditions if done even within 24 hours of onset.
- Should include Alteplase IV r-tPA treatment in eligible patients.
We have very fast and competent working team which provide you comfortable atmosphere and ease your nerves. Usual time of stay is around 2-3 Days.
Resume to work?
You can resume your work after 1 week if existing disease allows.

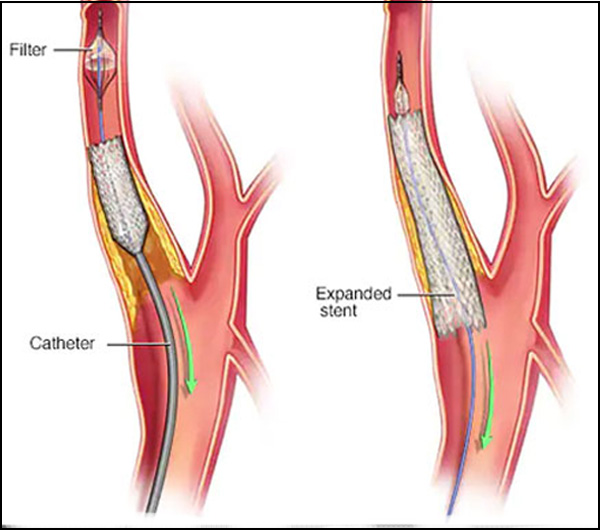
Carotid Artery Stenting:
The carotid artery is in the neck. There are usually two carotid arteries, one on each side of the neck The brain is supplied with blood from the two carotid arteries, along with two other arteries (the vertebral arteries), joining together to ensure the brain receives the blood that it needs.
Carotid artery disease causes strokes and carotid artery treatment is intended to reduce the risk of strokes in the future. The source of the blood clots may be the carotid artery causing stroke these clots get carried to the brain, and cause blockage of is artery, and the loss of blood to the area of the brain supplied by the artery. This may lead to permanent loss of brain function (this area dies). The greater the narrowing in the carotid artery, the more likely it is that this will cause clot, both now and in the future. For this reason, if symptoms occur, Stroke like, a doctor may recommend that this be treated. Sometimes the narrowing in the carotid may be very severe, but still not cause symptoms. In such circumstances, despite the fact that the narrow area has not caused problems, a doctor may advise that this be treated to try to prevent strokes. On the other hand, some blood clots can form in carotid arteries where the degree of narrowing is relatively slight. In this situation, treatment with drugs is usually recommended.
There are a number of stents that have been specially designed to be placed in the carotid artery. These have been designed specifically for the needs of this artery at the place where the artery divides. If disease should occur lower down in the carotid artery, then stents often used in other areas are suitable.
The specific stents made for the carotid artery are all “self expanding”. What this means is that they are made of metal, which springs open to a predefined size. The stents are pressed down onto their delivery system , where they are kept very thin to allow them to be passed to where they are needed. They are then released, in a controlled fashion, so that they fill the artery, and push the unwanted material out of the way. Often it is necessary to help the stent to open to the correct size, by finally expanding them with a balloon.
If there is disease either in the chest or up close to the brain, “balloon mounted” stents are often used. These will not expand to size on their own, so they are put onto the balloons and expanded up to size once this has been put into the correct place. The balloon is then deflated, leaving the stent in place. These stents have the advantage of being easier to place in the correct position, but the disadvantage of not being able to withstand compression. If these stents are compressed, they lose their shape and may cause the artery to block. They are, therefore, not suitable for use in the neck, where they may be compressed by outside forces and movement, where the self expanding stents are used.
Complications from carotid artery stenting can be considered either as occurring around the time of the procedure (within 30 days of the procedure) or later. The list below is not exhaustive, but rather is intended to explain the more common or worrying problems that may occur.
- The recognised early complications include:
- Stroke. This may cause significant disability (or even death), or may be relatively mild. It is uncommon, and in experienced hands happens in about 3-4% of cases, when there have been recent symptoms precipitating the procedure, or around 1-2% if the carotid artery disease is found incidentally. The majority of these events are more minor, but may leave a patient with severe disability (weakness affecting the arm and/or leg, or speech problems). Most of these events are caused by pieces of the disease becoming dislodged at the time of the procedure and causing problems with blood flow to the brain. In a small proportion of cases, the increased blood flow to the brain causes bleeding into the brain, and this is often a much more devastating event.
- Bleeding/bruising. Almost all patients have some bruising at the groin, where the tubes have been placed in order to get the stent into place. Occasionally this bleeding is significant and requires a further operation to stitch the area that is bleeding. This problem is more likely considering the medicines that are given to a patient during carotid artery stenting (blood thinning medications), however this is restricted by the use of devices used to stitch or plug the hole at the end of the procedure. Such devices are usually used by Radiologists performing carotid artery stents.
- Damage to the arteries. Very rarely the arteries which connect the access site in the groin to the carotid arteries are diseased and may become damaged during the passage of the tubes used for carotid artery stenting. This is most likely to occur in the artery at the groin used for entry of the tubes, and if it occurs may lead to poor blood flow into that leg. If this was to occur, it manifests itself by problems walking, or leg pain immediately after the carotid artery stenting procedure. This is one of the reasons why patients are usually kept in hospital for a while after the procedure, to ensure that should such problem occur, then they will be recognised and appropriately treated. It is possible that such complications could result in loss of that limb, but this is almost unheard of.
- Longer term the problems that can occur include:
- Stroke. Stroke can occur after both carotid artery stenting and the surgical alternative ( carotid endarterectomy). The likelihood of this occurring is approximately the same whichever procedure is undertaken, and is around 1% per year in the longer term. This likelihood will have been considered by the medical team when suggesting to a person that they may benefit from intervention. Intervention would not usually be considered, unless the person had disease which would be much more likely than this to cause stroke, and that the procedure could be expected to be performed with a less than 6% risk of stoke for disease causing symptoms and less than 3% for disease found incidently.
- Restenosis. This is the term used for re-narrowing of the area treated by the stent. Some people seem to be more prone to this happening, and may well have had the same problem irrespective of whether they were offered carotid artery stenting or endarterectomy. A minor degree of this is almost inevitable in all stents, but it rarely causes problems in terms of symptoms. If symptoms should occur then the area can be retreated, either by placement of another stent, or by removing the stent and treating the artery with an open operation (LINK TO VS SITE). This problem is particularly likely to happen if the reason for placing the stent in the first place was because the person had received x ray treatment to their neck in the past
As indicated in the section on the complications of carotid artery stenting, stroke can occur at the time of the procedure, and subsequently. A number of steps can be taken by the medical team to reduce the risk:
The procedure:
- The team of doctors, nurses and radiographers who are undertaking carotid artery stenting will be regularly performing the procedure and will be able to tell you, as a patient, what experience they have of doing the procedure. There are a number of studies which show that regular practice and experience of these (and other similar) procedures is useful in keeping the complications down to a minimum.
- A team of doctors will examine and assess people who may benefit from carotid artery stenting. They will only suggest this procedure having considered all of the options that are available.
- The arteries from the chest to the brain need to be imaged (pictures and scans), usually using a combination of ultrasound scanning, along with CT and/or MRI and/or angiography. The choice of the type of imaging will be dependent upon different patient features and needs. In this way the carotid stenting procedure can be planned and the equipment required predicted. Such imaging and planning will determine if carotid stenting is likely to be possible, and to predict the likely degree of difficulty (and therefore the likely risk of complications).
- Patients who undergo carotid artery stenting will have their medications optimised for the procedure. This usually means ensuring that they are taking a statin, and are taking dual antiplatelet medications (usually aspirin and Clopidogrel). Please see the section on treatments for carotid artery disease.
- Dedicated stents designed for use in the carotid artery are usually used. Please see the section on carotid artery stents.
- There are a series of specially designed devices, called “Cerebral Protection Devices” (sometimes shortened to CPD’s in some literature). These have been specifically designed to reduce the risk of stroke at the time of carotid artery stenting. There are a number of these available, and the individual devices can be found on the internet. So far no one device has been found to be more effective than another, and indeed there are some data which would question the effectiveness of these devices. If you are considering having a carotid stent fitted, it may be worthwhile asking your particular doctor if he/she is practiced at using these devices, and to discuss with him/her if it would be likely to be beneficial in your particular case.
All people who are known to have carotid artery disease will have their medications altered to try to reduce their risk of stroke or further stroke.
When the level of carotid artery disease goes above a critical level additional treatment is often recommended. This can be in the form of either an operation (carotid endarterectomy – see VS SITE) or carotid artery stenting. carotid artery stenting offer the potential benefit of preventing stokes in the future.
- Carotid stenting offers:
- Minimally invasive (“keyhole”) treatment
- Almost always done under local anaesthetic.
- Less likely to cause heart complications
- No problems with nerve damage in the neck
- Less significant bleeding problems.
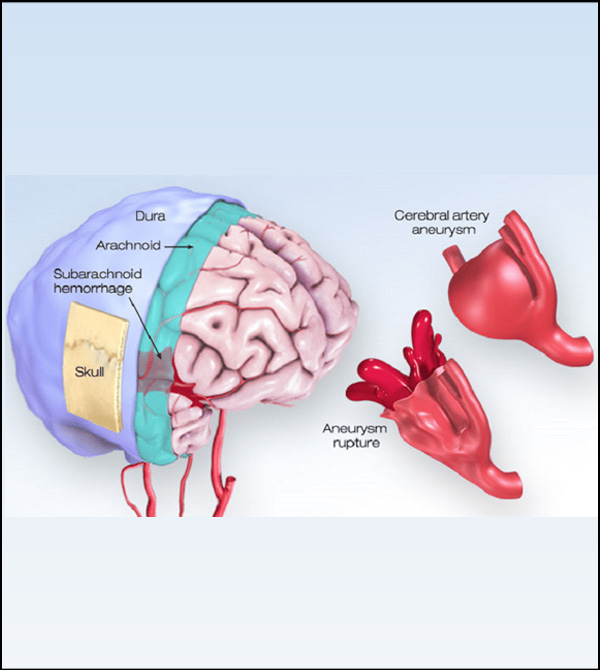
Cerebral Aneurysm:
An aneurysm is an abnormal outpouching of an artery's wall. Aneurysms affecting the arteries supplying the brain can cause a stroke. If the aneurysm ruptures, blood flows into the space surrounding the brain called the subarachnoid space. A patient with a subarachnoid hemorrhage usually suffers a severe headache followed by nausea, vomiting, irritation and lethargy. Double vision, neck stiffness, weakness, loss of sensation, and loss of consciousness can also occur.
Brain aneurysms are more common in adults than in children and more common in women than in men.
Some of these risk factors develop over time; others are present at birth.
- Risk factors that develop over time
- Older age
- Cigarette smoking
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Drug abuse, particularly the use of cocaine
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Risk factors present at birth
- Inherited connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, that weaken blood vessels
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Abnormally narrow aorta (coarctation of the aorta).
- Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (brain AVM)
- Family history of brain aneurysm, particularly a first-degree relative, such as a parent, brother, sister, or child.
- Ruptured aneurysm
A sudden, severe headache is the key symptom of a ruptured aneurysm. This headache is often described as the 'worst headache' ever experienced. - Sudden, extremely severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion
- 'Leaking' aneurysm
In some cases, an aneurysm may leak a slight amount of blood. This leaking (sentinel bleed) may cause only a: - Sudden, extremely severe headache A more severe rupture often follows leaking
- Unruptured aneurysm
An unruptured brain aneurysm may produce no symptoms, particularly if it's small. However, a larger unruptured aneurysm may press on brain tissues and nerves, possibly causing: - Pain above and behind one eye
- A dilated pupil
- Change in vision or double vision
- Numbness of one side of the face
If left untreated an aneurysm may rupture leading to life threatening bleeding and somtimes death
Seek immediate medical attention if you develop a:
Sudden, extremely severe headache
To diagnose a brain Aneurysms, your neurologist or Interventional Radiologist will review your symptoms and conduct a physical examination.
Your doctor may order one or more tests to diagnose your condition. Interventional Radiologists trained in brain and nervous system imaging usually conduct imaging tests.
Tests used to diagnose brain Aeurysms include:
- Cerebral arteriography
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
There are two basic approaches to treating an aneurysm:
- The traditional approach, a full fledge surgery which involves making a window in the skull to repair the aneurysm by surgically clipping it.
- Coil embolization, which is threading a small tube into the aneurysm through an artery in the brain and packing the aneurysm with platinum coils. through a small cut without need a an entire surgery
With this approach, small platinum coils are placed into the bulge of the aneurysm to seal it off while preserving the normal blood flow of the artery.
This procedure does not require a craniotomy or any incision on the head. The procedure is done in a radiology suite where angiograms are done. It is done under general anesthesia.
During the procedure, a small tube is placed through an artery in the groin. Small platinum coils are delivered to the aneurysm . They block off the ballooned part of the artery. The normal opening of the artery is left clear
We have very fast and competent working team which provide you comfortable atmosphere and ease your nerves. Usual time of stay is around 2-3 Days.
Resume to work?
You can resume your work very next day of the procedure preferably in 2- 3 days.